Radio: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Lo spettro radio == | == Lo spettro radio == | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Band name | |||
! Abbreviation | |||
! [[ITU Radio Bands|ITU band]] | |||
! Frequency<br />and<br />wavelength in air | |||
! Example uses | |||
|- | |||
| [[Tremendously low frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| TLF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| < 3 [[Hertz|Hz]]<br />> 100,000 km | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| Natural and artificial electromagnetic noise | |||
|- | |||
| [[Extremely low frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| ELF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 3–30 Hz<br />100,000 km – 10,000 km | |||
| style="text-align:center;"|[[Communication with submarines]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Super low frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| SLF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 30–300 Hz<br />10,000 km – 1000 km | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| Communication with submarines | |||
|- | |||
| [[Ultra low frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| ULF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 300–3000 Hz<br />1000 km – 100 km | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| Submarine communication, [[Through the earth mine communications|communication within mines]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Very low frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| VLF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| 4 | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 3–30 kHz<br />100 km – 10 km | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| [[Radio navigation|Navigation]], [[radio clock|time signals]], submarine communication, wireless [[heart rate monitor]]s, [[geophysics]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Low frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| LF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| 5 | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 30–300 kHz<br />10 km – 1 km | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| Navigation, [[Radio clock|clock time signals]], AM [[longwave]] broadcasting (Europe and parts of Asia), [[RFID]], [[amateur radio]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Medium frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| MF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| 6 | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 300–3000 kHz<br />1 km – 100 m | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| [[AM radio|AM]] (medium-wave) broadcasts, amateur radio, [[Avalanche#Beacons|avalanche beacons]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[High frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| HF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| 7 | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 3–30 MHz<br />100 m – 10 m | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| [[Shortwave]] broadcasts, [[citizens' band radio]], amateur radio and [[over-the-horizon]] aviation communications, [[RFID]], [[over-the-horizon radar]], [[automatic link establishment]] (ALE) / [[Near Vertical Incidence Skywave|near-vertical incidence skywave]] (NVIS) radio communications, [[marine and mobile radio telephony]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Very high frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| VHF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| 8 | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 30–300 MHz<br />10 m – 1 m | |||
| style="text-align:center;" | [[FM radio|FM]], [[television]] broadcasts and line-of-sight ground-to-aircraft and aircraft-to-aircraft communications, land mobile and maritime mobile communications, amateur radio, [[weather radio]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Ultra high frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| UHF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| 9 | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 300–3000 MHz<br />1 m – 100 mm | |||
| style="text-align:center;" | Television broadcasts, [[microwave oven]], [[microwave]] devices/communications, [[radio astronomy]], [[mobile phone]]s, [[wireless LAN]], [[Bluetooth]], [[ZigBee]], [[GPS]] and two-way radios such as land mobile, [[Family Radio Service|FRS]] and [[GMRS]] radios, amateur radio | |||
|- | |||
| [[Super high frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| SHF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| 10 | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 3–30 GHz<br />100 mm – 10 mm | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| Radio astronomy, microwave devices/communications, wireless LAN, most modern [[radar]]s, [[communications satellite]]s, satellite television broadcasting, [[direct-broadcast satellite|DBS]], amateur radio | |||
|- | |||
| [[Extremely high frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| EHF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| 11 | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 30–300 GHz<br />10 mm – 1 mm | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| Radio astronomy, high-frequency [[microwave radio relay]], microwave [[remote sensing]], amateur radio, [[Active Denial System|directed-energy weapon]], [[millimeter wave scanner]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Terahertz]] or [[Tremendously high frequency]] | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| THz or THF | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| 12 | |||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 300–3,000 GHz<br />1 mm – 100 {{mu}}m | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| Terahertz imaging – a potential replacement for X-rays in some medical applications, ultrafast molecular dynamics, [[condensed-matter physics]], [[terahertz time-domain spectroscopy]], terahertz computing/communications, sub-mm remote sensing, amateur radio | |||
|} | |||
Revision as of 14:01, 3 July 2015
Lo spettro elettromagnetico
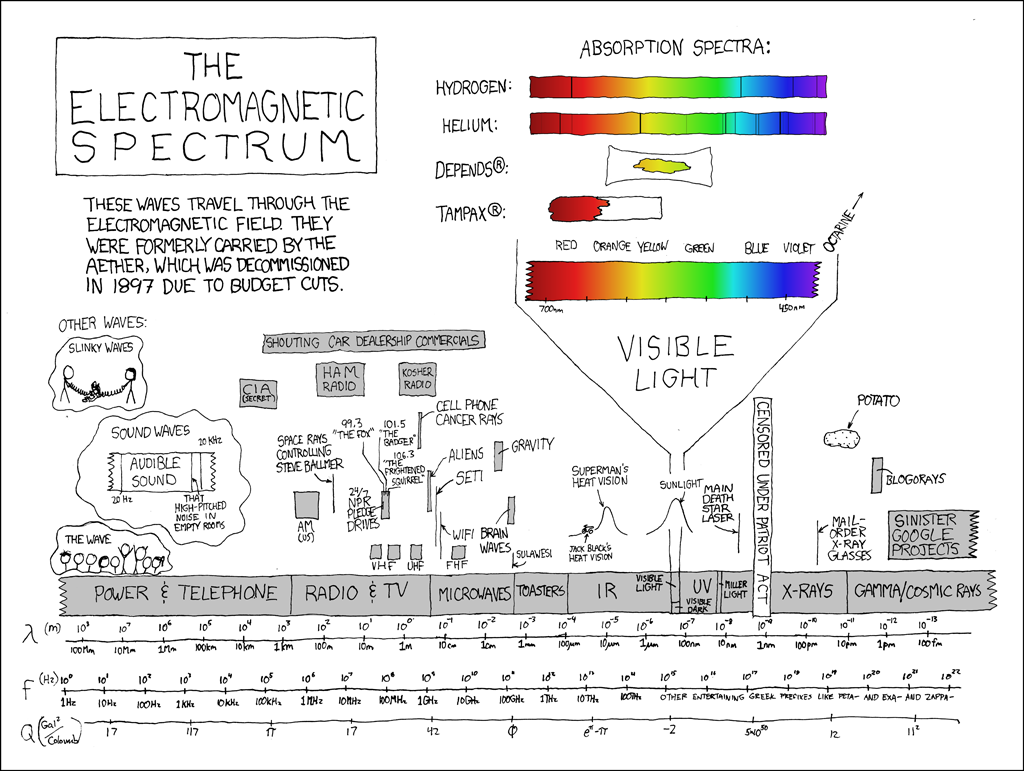
atmosfera
Lo spettro radio
| Band name | Abbreviation | ITU band | Frequency and wavelength in air |
Example uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tremendously low frequency | TLF | < 3 Hz > 100,000 km |
Natural and artificial electromagnetic noise | |
| Extremely low frequency | ELF | 3–30 Hz 100,000 km – 10,000 km |
Communication with submarines | |
| Super low frequency | SLF | 30–300 Hz 10,000 km – 1000 km |
Communication with submarines | |
| Ultra low frequency | ULF | 300–3000 Hz 1000 km – 100 km |
Submarine communication, communication within mines | |
| Very low frequency | VLF | 4 | 3–30 kHz 100 km – 10 km |
Navigation, time signals, submarine communication, wireless heart rate monitors, geophysics |
| Low frequency | LF | 5 | 30–300 kHz 10 km – 1 km |
Navigation, clock time signals, AM longwave broadcasting (Europe and parts of Asia), RFID, amateur radio |
| Medium frequency | MF | 6 | 300–3000 kHz 1 km – 100 m |
AM (medium-wave) broadcasts, amateur radio, avalanche beacons |
| High frequency | HF | 7 | 3–30 MHz 100 m – 10 m |
Shortwave broadcasts, citizens' band radio, amateur radio and over-the-horizon aviation communications, RFID, over-the-horizon radar, automatic link establishment (ALE) / near-vertical incidence skywave (NVIS) radio communications, marine and mobile radio telephony |
| Very high frequency | VHF | 8 | 30–300 MHz 10 m – 1 m |
FM, television broadcasts and line-of-sight ground-to-aircraft and aircraft-to-aircraft communications, land mobile and maritime mobile communications, amateur radio, weather radio |
| Ultra high frequency | UHF | 9 | 300–3000 MHz 1 m – 100 mm |
Television broadcasts, microwave oven, microwave devices/communications, radio astronomy, mobile phones, wireless LAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee, GPS and two-way radios such as land mobile, FRS and GMRS radios, amateur radio |
| Super high frequency | SHF | 10 | 3–30 GHz 100 mm – 10 mm |
Radio astronomy, microwave devices/communications, wireless LAN, most modern radars, communications satellites, satellite television broadcasting, DBS, amateur radio |
| Extremely high frequency | EHF | 11 | 30–300 GHz 10 mm – 1 mm |
Radio astronomy, high-frequency microwave radio relay, microwave remote sensing, amateur radio, directed-energy weapon, millimeter wave scanner |
| Terahertz or Tremendously high frequency | THz or THF | 12 | 300–3,000 GHz 1 mm – 100 Template:Mum |
Terahertz imaging – a potential replacement for X-rays in some medical applications, ultrafast molecular dynamics, condensed-matter physics, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy, terahertz computing/communications, sub-mm remote sensing, amateur radio |